In recent years, the financial markets have been volatile and unpredictable, with numerous factors affecting investor sentiment. One of the most significant events that can impact the stock market is a credit downgrade of the United States. This article explores the potential effects of such a downgrade on stocks and examines historical examples to provide insight into how investors can navigate this challenging situation.
Understanding the Credit Downgrade
A credit downgrade occurs when a credit rating agency, such as Moody's, Standard & Poor's, or Fitch Ratings, lowers the credit rating of a country's government bonds. This typically happens when the agency believes that the country is at a higher risk of defaulting on its debt obligations. For the United States, a credit downgrade would be a major event, as it would be the first time in history that the country's credit rating has been downgraded.
The Immediate Impact on Stocks
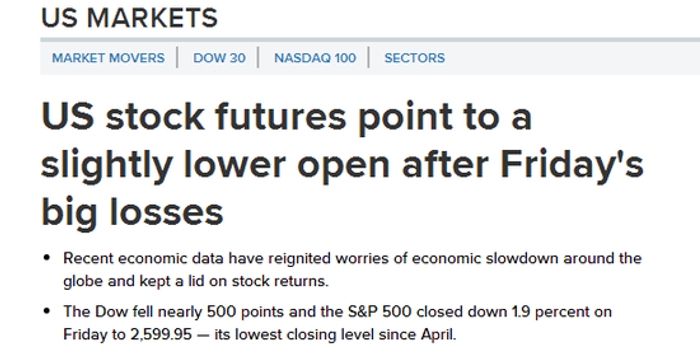
An immediate impact of a US credit downgrade on stocks is likely to be a significant sell-off. Investors tend to be risk-averse in times of uncertainty, and a credit downgrade can be seen as a sign of economic instability. This can lead to widespread selling across various sectors, as investors seek to protect their portfolios.
Long-term Effects on the Stock Market
While the immediate impact of a credit downgrade is often negative, the long-term effects on the stock market can vary. Historically, the stock market has recovered from credit downgrades, but it may take several months or even years. During this period, investors may experience increased volatility and uncertainty.
Impact on Specific Sectors
A credit downgrade can have varying effects on different sectors of the stock market. For example:
- Financial Sector: The financial sector is likely to be one of the most affected, as a credit downgrade can lead to higher borrowing costs for financial institutions.
- Consumer Discretionary Sector: Companies in the consumer discretionary sector, such as retailers and restaurants, may also be negatively impacted, as consumer confidence tends to decline during economic uncertainty.
- Technology Sector: The technology sector may be less affected, as these companies often have a global presence and may be less dependent on the US economy.
Historical Examples
To illustrate the potential impact of a credit downgrade on stocks, let's examine two historical examples:
- 2011 US Credit Downgrade: In 2011, the United States faced a credit downgrade from AAA to AA+ by Standard & Poor's. This event led to a significant sell-off in the stock market, with the S&P 500 falling nearly 10% over a two-week period. However, the market eventually recovered, and the S&P 500 reached an all-time high in 2013.
- European Debt Crisis: The European debt crisis in 2010-2012 also provided valuable insights into the impact of a credit downgrade. Countries such as Greece, Ireland, and Portugal faced credit downgrades, leading to significant sell-offs in their respective stock markets. However, the overall impact on the global stock market was less severe compared to the 2011 US credit downgrade.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a credit downgrade of the United States can have a significant impact on the stock market, both in the short and long term. While the immediate impact is often negative, the market may eventually recover. Investors should monitor economic indicators and stay informed about credit ratings to make informed decisions. By understanding the potential effects of a credit downgrade, investors can better navigate the complexities of the stock market and protect their portfolios.
google stock price
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....