Introduction: In the vast world of investments, US government bonds and stocks are two popular choices for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios. Both offer unique advantages and risks, making it crucial for investors to understand the differences between them. In this article, we will explore the key characteristics of US government bonds and stocks, compare their performance, and help you make an informed decision about which one suits your investment goals.
Understanding US Government Bonds:
What are US Government Bonds? US government bonds are debt securities issued by the U.S. government to finance its spending needs. These bonds are considered one of the safest investments due to the government's strong credit rating.
Key Features:
- Low Risk: US government bonds are considered risk-free, as the government has the authority to tax and print money to repay its debts.
- Fixed Income: Investors receive regular interest payments, known as coupons, at a fixed rate.
- Maturity: Bonds have a maturity date, at which point the principal amount is repaid.
Understanding Stocks:
What are Stocks? Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder and have a claim on the company's profits and assets.
Key Features:
- Potential for Growth: Stocks have the potential to offer higher returns than bonds, especially over the long term.
- Dividends: Some companies distribute dividends to shareholders, which can provide additional income.
- Volatility: Stocks are more volatile than bonds, meaning their prices can fluctuate widely.
Comparing Performance:
Historical Returns: Historically, stocks have outperformed bonds in terms of returns. However, this does not guarantee future performance. Stocks have provided higher returns due to their potential for capital appreciation and dividends, while bonds have offered lower returns but with lower risk.
Risk vs. Reward: Investors seeking lower risk and steady income may prefer bonds, while those willing to accept higher risk for potentially higher returns may opt for stocks.
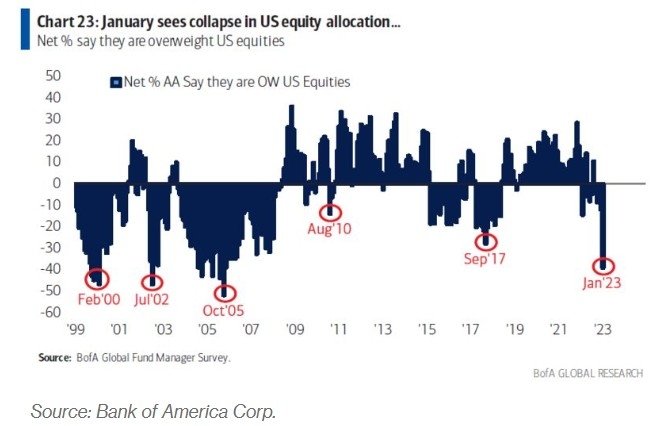
Case Study: Consider the performance of the S&P 500 index, a widely followed benchmark for stocks, and the U.S. Treasury bond index, representing government bonds. Over the past 30 years, the S&P 500 has returned an average of 7% per year, while the U.S. Treasury bond index has returned an average of 3% per year. This demonstrates the potential for higher returns in stocks, but with increased risk.
Conclusion: In conclusion, US government bonds and stocks offer distinct investment opportunities with different risk and return profiles. Understanding the key characteristics and performance of both can help investors make informed decisions about their portfolios. Whether you prioritize stability and income or growth and potential capital appreciation, choosing the right mix of bonds and stocks is essential for achieving your investment goals.

us stock market today
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....