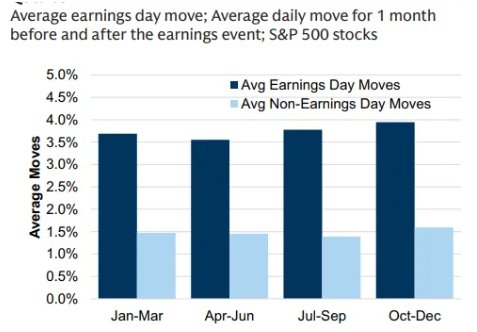
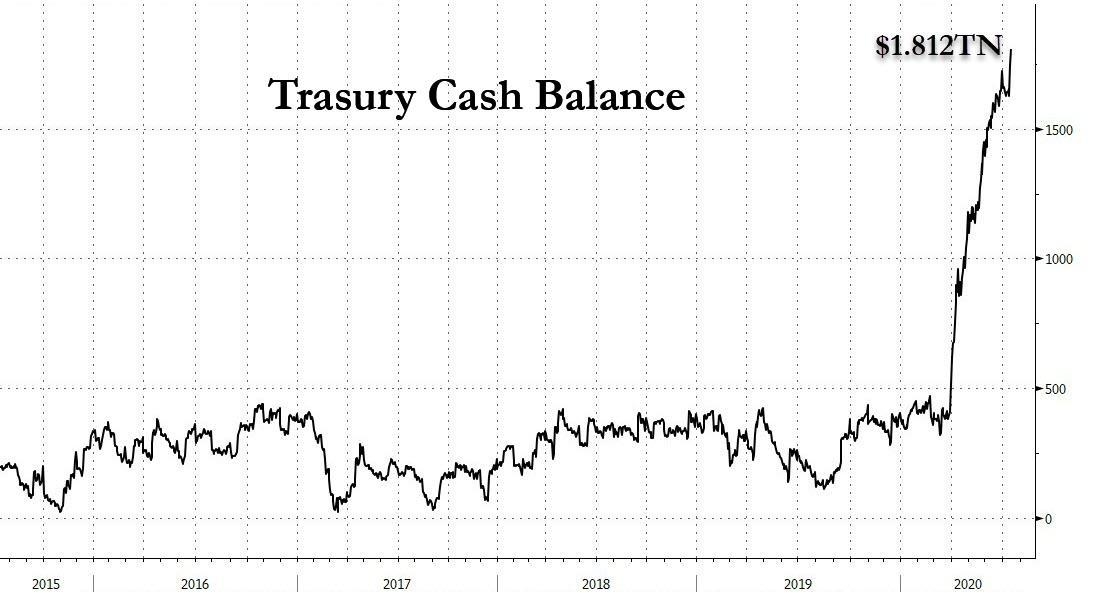
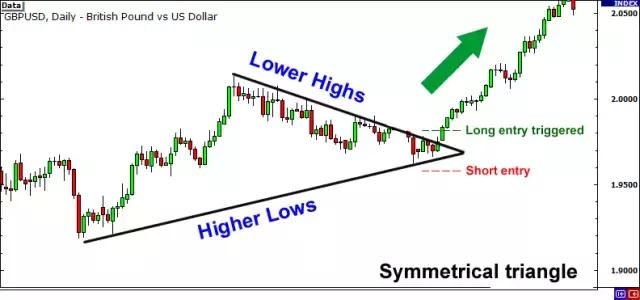
The stock market crash of 2008 was a monumental event that had a profound impact on the United States and the global economy. This article delves into the causes, effects, and aftermath of this catastrophic event, shedding light on the lessons learned and the lasting legacy it left behind.
Causes of the Stock Market Crash
The 2008 stock market crash was primarily triggered by a combination of factors, including the subprime mortgage crisis, excessive risk-taking by financial institutions, and government regulations that failed to prevent predatory lending practices. These elements created a toxic environment that ultimately led to the collapse of the housing market, the banking sector, and the broader financial system.
Subprime Mortgage Crisis
One of the root causes of the crash was the subprime mortgage crisis. Lenders had begun offering mortgages to borrowers with poor credit histories, leading to a rapid increase in defaults. This, in turn, caused the value of mortgage-backed securities to plummet, creating a ripple effect that spread throughout the financial system.
Excessive Risk-Taking
Financial institutions took on excessive risks by investing heavily in these toxic assets, underestimating the potential consequences. They engaged in speculative trading and complex financial instruments, often without fully understanding the risks involved. This behavior exacerbated the instability in the financial system.
Government Regulations
Government regulations, or the lack thereof, played a significant role in the crisis. Regulatory bodies failed to enforce strict lending standards, allowing predatory lenders to thrive. Moreover, the financial sector had significant influence over policymakers, contributing to a regulatory environment that favored their interests over those of the public.
Effects of the Stock Market Crash
The 2008 stock market crash had far-reaching effects on the United States, impacting various aspects of the economy and society.
Economic Consequences
The crash led to a severe recession, characterized by high unemployment rates, falling wages, and a decrease in consumer spending. Businesses struggled to stay afloat, leading to layoffs and a reduction in investment. The stock market lost trillions of dollars in value, devastating retirement portfolios and savings.
Social Consequences
The crash had a profound impact on individuals and families across the nation. Many homeowners faced foreclosure, leading to a rise in homelessness and a loss of community stability. Mental health issues, including depression and anxiety, also surged as people grappled with the economic turmoil.

Policy Reforms
In response to the crisis, the government implemented several reforms aimed at preventing another such event. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was passed in 2010, imposing stricter regulations on financial institutions and increasing transparency in the financial system.
Lessons Learned
The 2008 stock market crash served as a wake-up call for policymakers, investors, and regulators. Key lessons learned from the crisis include the importance of robust financial regulation, the need for transparency in financial markets, and the significance of addressing income inequality.
Conclusion
The 2008 stock market crash was a devastating event that had a profound impact on the United States. By understanding the causes, effects, and lessons learned from this crisis, we can strive to prevent similar occurrences in the future and build a more resilient financial system.
us stock market today
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....