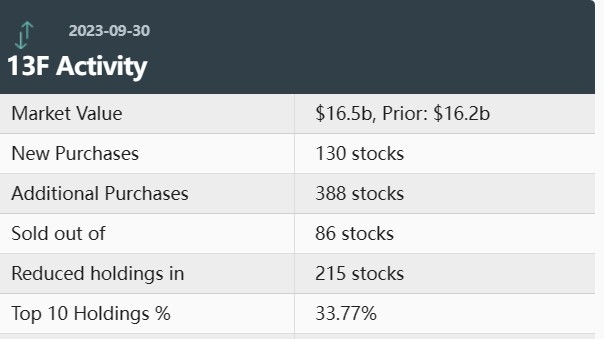
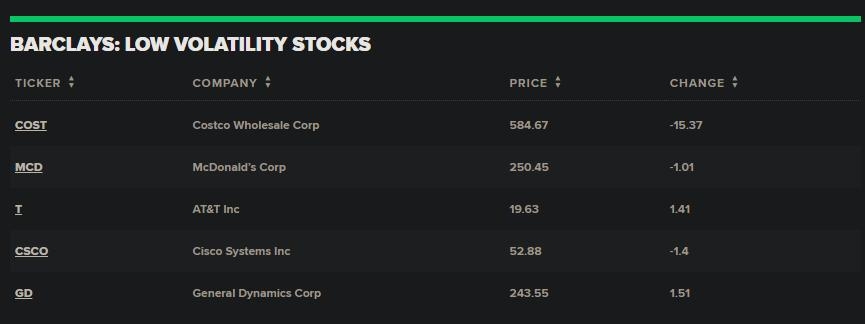
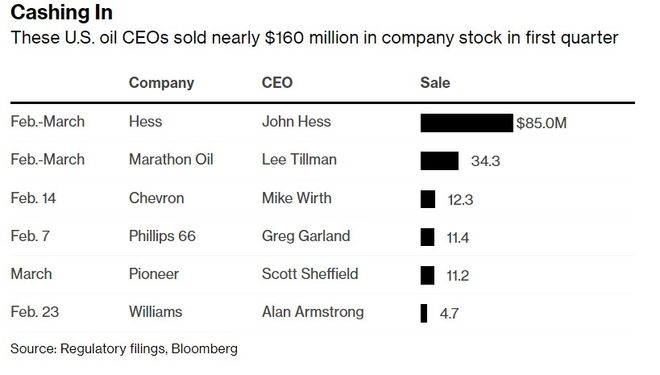
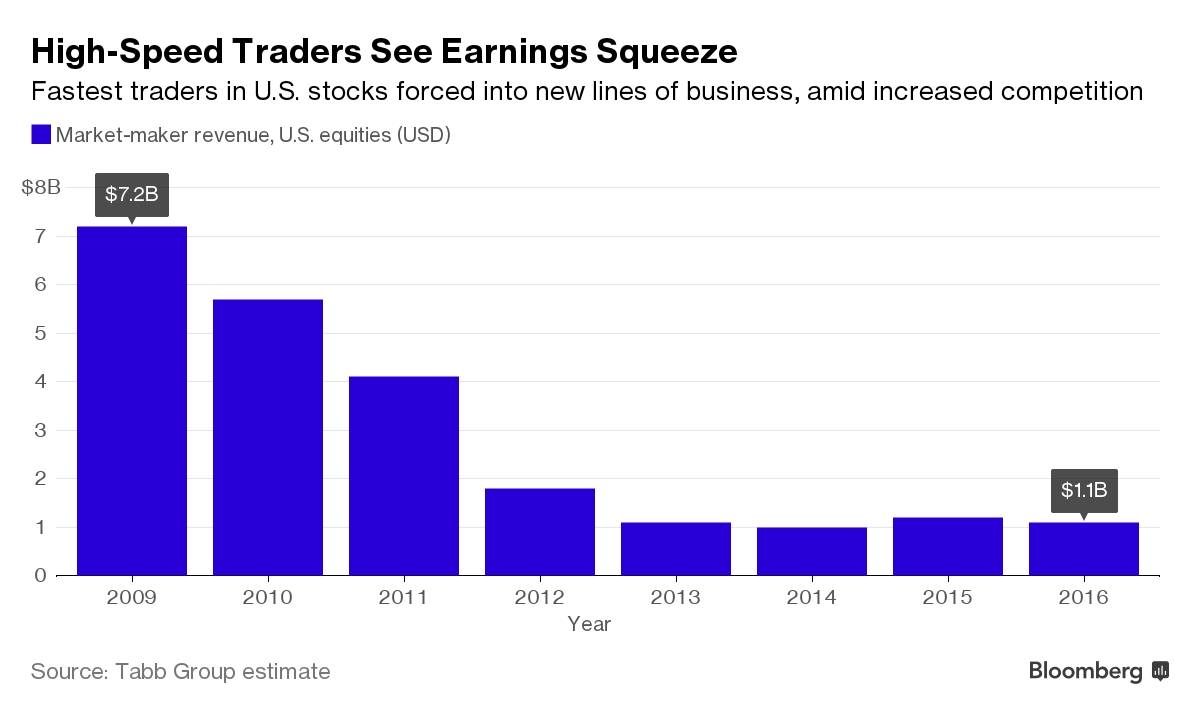
Are you looking to invest in U.S. stocks but feel overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available? Look no further! Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer a convenient and diversified way to invest in the U.S. stock market. This article will provide an in-depth guide on how to choose the right ETFs for your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Understanding ETFs

An ETF is a type of investment fund that trades on an exchange, much like a stock. ETFs are designed to track the performance of a specific index, sector, or asset class. Unlike mutual funds, which are priced at the end of the trading day, ETFs are priced continuously throughout the trading day.
Benefits of Investing in U.S. Stocks through ETFs
- Diversification: By investing in an ETF, you gain exposure to a wide range of companies across various sectors and industries, reducing your risk compared to investing in individual stocks.
- Lower Costs: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them a cost-effective way to invest.
- Liquidity: ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices, providing investors with flexibility and liquidity.
- Transparency: The holdings of an ETF are disclosed daily, making it easier for investors to understand what they are investing in.
Types of U.S. Stock ETFs
- Index ETFs: These ETFs track broad market indices like the S&P 500, Nasdaq 100, or Russell 2000.
- Sector ETFs: These ETFs focus on specific sectors, such as technology, healthcare, or financials.
- Region ETFs: These ETFs track the performance of stocks in a particular geographic region, such as the U.S., Europe, or emerging markets.
- Commodity ETFs: These ETFs provide exposure to commodities like gold, oil, or natural gas.
How to Choose the Right U.S. Stock ETF
- Investment Goals: Determine your investment goals and risk tolerance. Are you looking for long-term growth or income?
- Diversification: Consider how the ETF fits into your overall investment portfolio. Ensure it offers diversification across various sectors and industries.
- Expense Ratio: Compare the expense ratios of different ETFs to find the most cost-effective option.
- Performance: Review the historical performance of the ETF to gauge its track record.
- Fundamentals: Analyze the underlying companies in the ETF to ensure they meet your criteria for quality and growth potential.
Case Study: Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
One of the most popular U.S. stock ETFs is the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO). This ETF tracks the S&P 500 index, representing the 500 largest companies listed on U.S. exchanges. With an expense ratio of just 0.04%, VOO is an excellent choice for investors seeking a low-cost, diversified way to invest in U.S. stocks. Over the past decade, VOO has delivered a compound annual growth rate of approximately 14%, outperforming many actively managed mutual funds.
Conclusion
Investing in U.S. stocks through ETFs offers numerous advantages, including diversification, lower costs, and liquidity. By understanding the different types of U.S. stock ETFs and how to choose the right one for your investment goals, you can effectively build a well-diversified portfolio and potentially achieve long-term financial success.
google stock price
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....