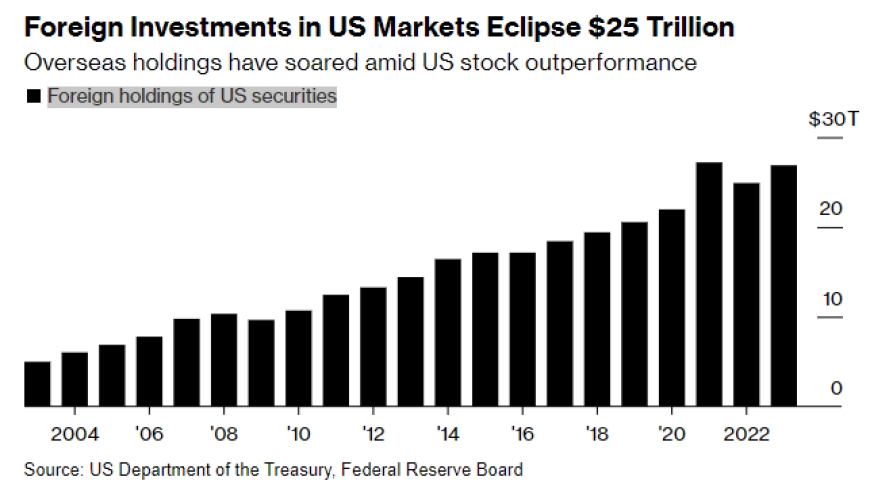
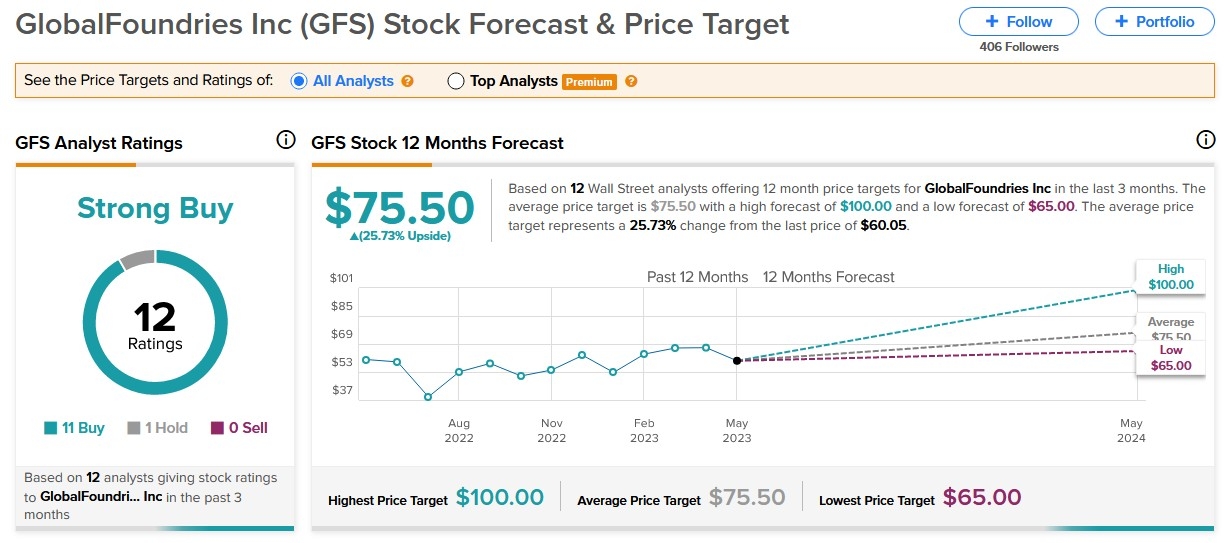
In the vast landscape of the U.S. stock market, investors often seek out companies that offer significant value. These are known as "deep value stocks." These companies, often overlooked by the market, provide a unique opportunity for investors to capitalize on their undervalued assets. This article delves into the concept of deep value stocks, their characteristics, and how they can be identified. We will also examine some real-world examples to illustrate the potential of this investment strategy.
What are Deep Value Stocks?
Deep value stocks are companies that are trading at significantly below their intrinsic value. This means that the market is undervaluing the true worth of the company, providing investors with a potential opportunity to purchase shares at a discounted price. These stocks are often found in sectors that are out of favor or have faced temporary setbacks, leading to a negative market sentiment.
Characteristics of Deep Value Stocks
Several key characteristics define deep value stocks:

- Low Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B Ratio): This ratio compares the market value of a company to its book value. Deep value stocks typically have a P/B ratio below 1, indicating that the market value is less than the company's net assets.
- High Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio): While a high P/E ratio might suggest overvaluation, a very high P/E ratio in the context of deep value stocks can indicate that the market is undervaluing the company.
- Strong Financial Health: Despite their low market value, deep value stocks should still possess strong financial health, including low debt levels and positive cash flow.
- Long-Term Perspective: Investing in deep value stocks requires a long-term perspective, as it may take time for the market to recognize the true value of the company.
Identifying Deep Value Stocks
Identifying deep value stocks requires thorough research and analysis. Here are some steps to consider:
- Sector Analysis: Look for sectors that are currently out of favor or facing short-term challenges.
- Financial Analysis: Evaluate the company's financial statements, including its balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
- Market Sentiment: Understand the market sentiment surrounding the company and its industry.
- Management Analysis: Assess the quality of the company's management team and their track record.
Real-World Examples
Several notable companies have been classified as deep value stocks in the past:
- General Electric (GE): Despite facing numerous challenges, GE has been considered a deep value stock at various points in time. Its low market value relative to its book value and strong financial health have made it an attractive investment for value investors.
- Ford Motor Company: Ford has faced competition from foreign automakers, but its strong financial position and low market value have made it a potential deep value investment.
Conclusion
Investing in deep value stocks can be a rewarding strategy, but it requires careful analysis and a long-term perspective. By identifying companies that are undervalued by the market, investors can potentially benefit from significant returns. However, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and understand the risks associated with this investment approach.
us stock market today live cha
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....