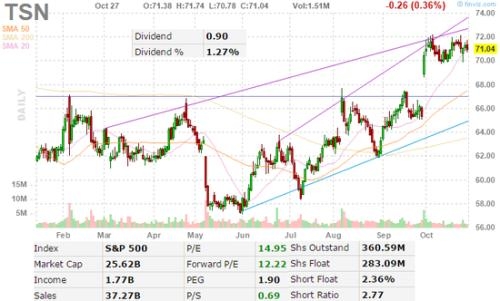
Are you a shareholder in a US stock? Do you know if the dividends you receive are qualified? In this article, we'll delve into what qualifies as a dividend, how they are taxed, and the benefits of receiving qualified dividends. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, this information is crucial for maximizing your investment returns.
What are Qualified Dividends?
Qualified Dividends refer to dividends that meet specific criteria set by the IRS. To be classified as a qualified dividend, the stock must be a U.S. corporation stock, and the dividend must be paid to shareholders who have held the stock for a minimum of 60 days during the 121-day period that includes the ex-dividend date.
Key Criteria for Qualified Dividends:
- U.S. Corporation Stock: The stock must be issued by a U.S. corporation.
- Holding Period: Shareholders must hold the stock for at least 60 days during the 121-day period that includes the ex-dividend date.
- Dividend Rate: The dividend rate must be at least 5% of the fair market value of the stock on the date of the ex-dividend.
Tax Implications of Qualified Dividends
One of the primary benefits of receiving qualified dividends is the lower tax rate compared to non-qualified dividends. Qualified dividends are taxed at the lower capital gains tax rates, which are typically lower than the ordinary income tax rates.
Benefits of Qualified Dividends:
- Lower Tax Rate: Qualified dividends are taxed at the lower capital gains tax rates, which can result in significant tax savings.
- Investment Growth: By receiving qualified dividends, shareholders can reinvest the dividends to potentially grow their investment further.
- Tax Efficiency: Qualified dividends are a tax-efficient way to receive income from investments.
Case Study:
Let's consider an example to illustrate the benefits of qualified dividends. Imagine you own 100 shares of a U.S. corporation stock that pays a
How to Determine if a Dividend is Qualified:
To determine if a dividend is qualified, you can check the ex-dividend date and the holding period. If the stock meets the criteria mentioned earlier, the dividend is likely to be classified as a qualified dividend.
Conclusion:
Understanding the concept of qualified dividends is crucial for investors seeking to maximize their investment returns. By taking advantage of the lower tax rate and reinvesting the dividends, shareholders can potentially grow their investments further. Always consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure you are taking full advantage of the benefits of qualified dividends.
us stock market today
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....