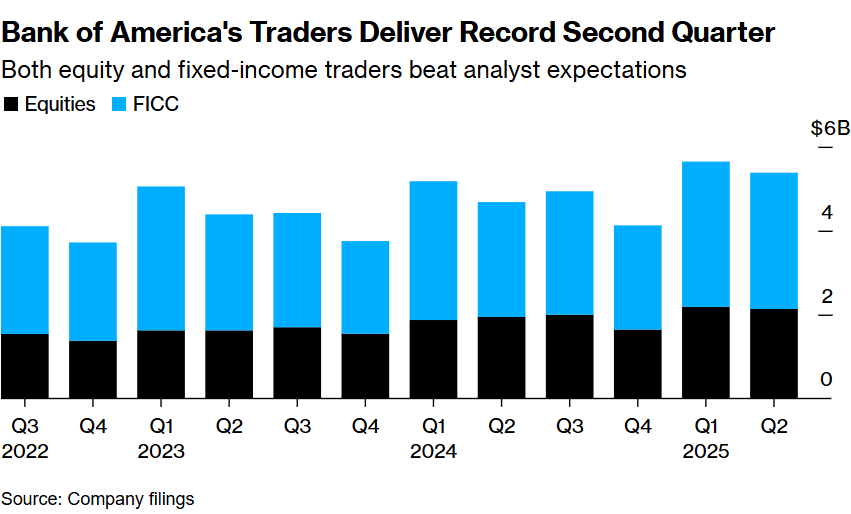
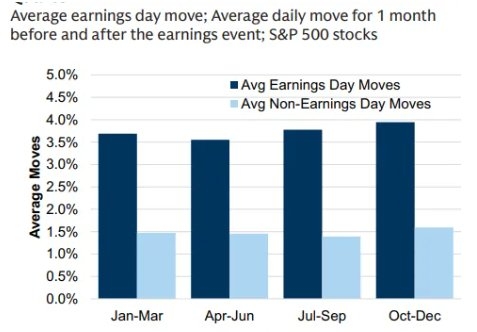
In the ever-evolving landscape of the real estate market, understanding the historical data of the US housing stock is crucial for investors, developers, and policymakers. This article delves into the historical trends, key figures, and significant shifts in the US housing market, providing a comprehensive overview for anyone interested in this vital sector.
Historical Overview of the US Housing Stock
The US housing stock has undergone significant changes over the years, reflecting broader economic, social, and demographic shifts. To appreciate the current state of the market, it's essential to examine its historical trajectory.
The Early 20th Century
In the early 20th century, the US housing stock was predominantly characterized by single-family homes, often built on large lots. The post-World War II era saw a surge in suburban development, driven by the construction of new highways and the rise of the automobile. This period marked the beginning of the "suburbanization" trend, which continued to shape the US housing market for decades.
The Mid-20th Century
The mid-20th century saw the emergence of "tract housing," a style of development where homes were built in large, standardized tracts. This approach allowed for mass production and reduced construction costs, making homeownership more accessible to the middle class. During this period, the US housing stock expanded rapidly, with an increasing number of Americans enjoying the benefits of homeownership.
The Late 20th Century and Early 21st Century
In the late 20th century and early 21st century, the US housing market experienced a series of booms and busts. The late 1980s and early 1990s saw a surge in housing prices, driven by low-interest rates and speculative investment. However, the bubble burst in the early 1990s, leading to a housing market downturn.
The late 2000s witnessed another housing crisis, sparked by the subprime mortgage crisis. This event had a profound impact on the US housing stock, leading to a significant decline in housing prices and a rise in foreclosures.
Key Historical Data Points
Several key data points highlight the evolution of the US housing stock:
The Number of Homes Built
The number of homes built in the US has fluctuated over the years, reflecting economic cycles and demographic trends. For example, the early 20th century saw a steady increase in the number of homes built, while the late 20th century and early 21st century experienced periods of rapid growth followed by downturns.
The Average Home Size
The average size of homes in the US has also changed over time. In the early 20th century, homes were typically smaller, with an average size of around 1,000 square feet. By the late 20th century, the average home size had doubled, reaching around 2,000 square feet.
The Homeownership Rate
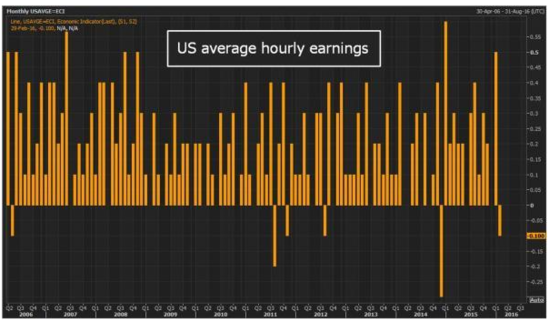
The homeownership rate in the US has been a significant indicator of the health of the housing market. In the early 20th century, the homeownership rate was around 40%. By the late 20th century, it had reached a peak of nearly 70%, before falling back to around 65% in recent years.
Case Studies: The Great Depression and the Subprime Mortgage Crisis
Two notable case studies in the US housing market are the Great Depression and the subprime mortgage crisis.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression of the 1930s had a profound impact on the US housing stock. With soaring unemployment and falling incomes, many homeowners defaulted on their mortgages, leading to a significant increase in foreclosures. The government responded by implementing various programs to stabilize the housing market, including the creation of the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the establishment of the Home Owners' Loan Corporation (HOLC).
The Subprime Mortgage Crisis
The subprime mortgage crisis of the late 2000s had a similarly devastating impact on the US housing market. The crisis was caused by a combination of factors, including predatory lending practices, excessive risk-taking by financial institutions, and a lack of regulation. The resulting housing market downturn led to a significant decline in home prices and a rise in foreclosures, similar to the Great Depression.
In conclusion, understanding the historical data of the US housing stock is essential for anyone interested in the real estate market. By examining key trends and data points, we can gain valuable insights into the factors that have shaped the US housing market over the years.
us stock market today
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....