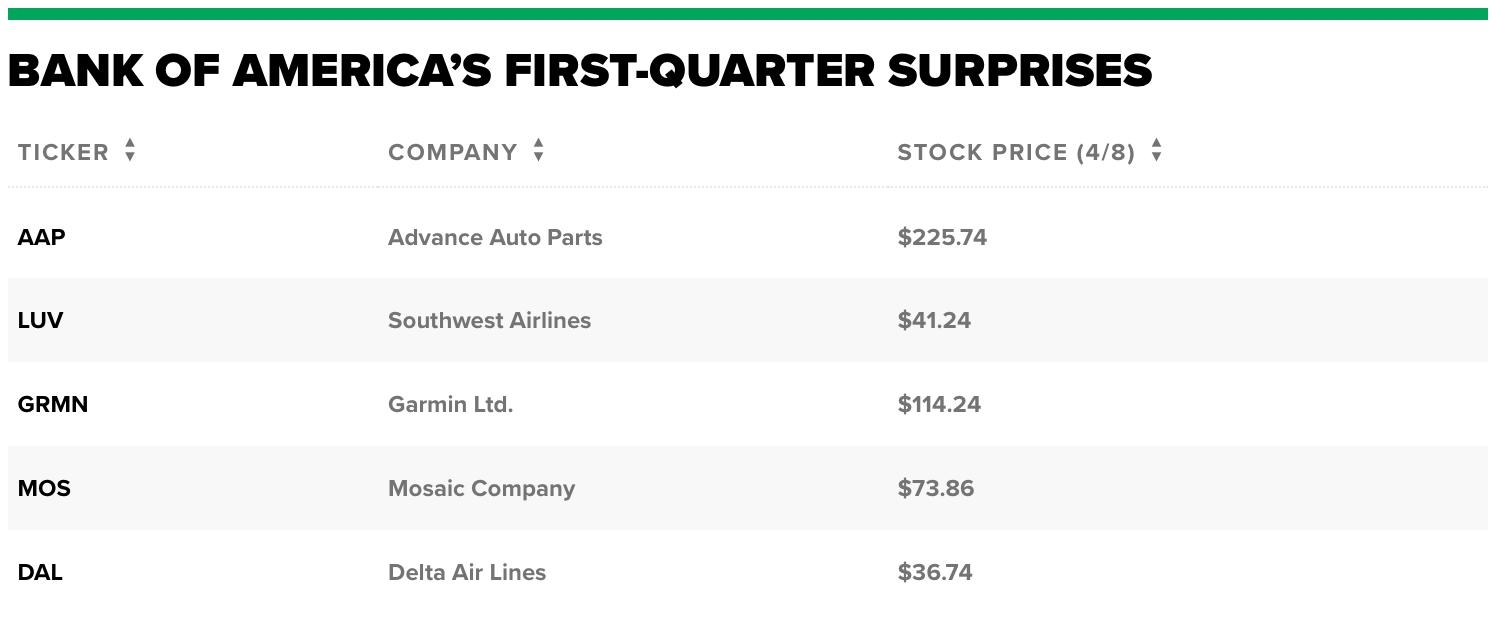
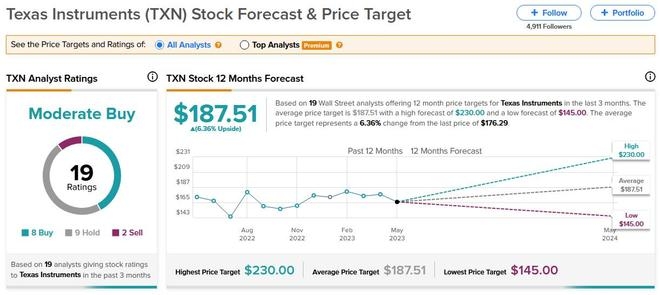
Introduction
The tragic events of September 11, 2001, had a profound impact on the United States, and the nation's stock market was no exception. The day that changed everything not only led to the loss of thousands of lives but also sent shockwaves through the financial sector. This article delves into the immediate and long-term effects of September 11 on the U.S. stock market, analyzing the aftermath and the subsequent recovery.
Immediate Impact
The day of the attacks, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation system (NASDAQ) were closed. This marked the first time the markets had been shut down since 1933, following the Great Depression. When the markets reopened four days later, the S&P 500 dropped by 7.1%, and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fell by 6.9%. These were the largest one-day declines since the Great Depression.
Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of September 11 on the stock market were complex and varied. Here are some of the key impacts:
1. Decline in Stock Prices
Following the attacks, there was a significant decline in stock prices. The S&P 500 fell by approximately 20% over the next three months, and the DJIA lost about 13%. This decline was driven by a combination of fear, uncertainty, and the economic downturn that followed.
2. Increased Government Spending
The aftermath of September 11 led to an increase in government spending on defense and security. This increase in spending helped offset some of the economic losses and supported the recovery of the stock market.
3. Shift in Investment Priorities
Investors began to reassess their investment strategies in the wake of September 11. Many shifted their focus from high-risk, high-reward investments to more stable, lower-risk assets. This shift helped stabilize the stock market in the long term.
4. The Birth of the Homeland Security Department
The establishment of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) following the attacks had a significant impact on the stock market. The creation of the DHS led to increased spending on defense and security, which in turn supported the growth of defense-related stocks.

Case Studies
One notable case study is the performance of United Airlines stock in the aftermath of September 11. Following the attacks, United's stock price fell by approximately 50%. However, over the next few years, the stock began to recover, thanks in part to increased government spending on defense and security.
Conclusion
The attacks of September 11, 2001, had a profound impact on the U.S. stock market. While the immediate aftermath was marked by significant declines, the long-term effects were more complex. The stock market eventually recovered, but the lessons learned from September 11 continue to shape investment strategies and government policies to this day.
us stock market today
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....