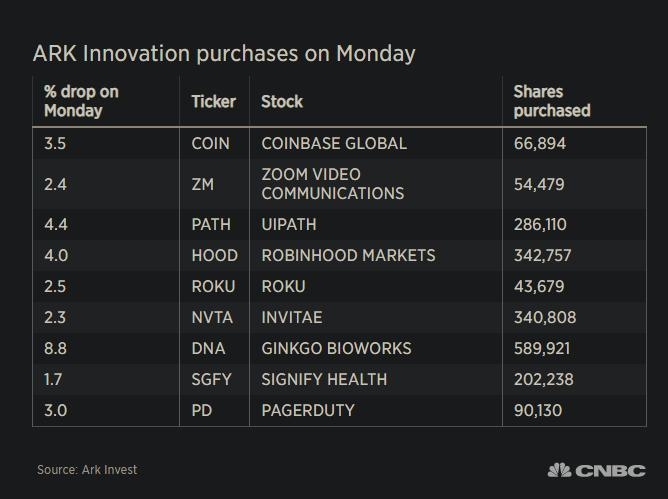
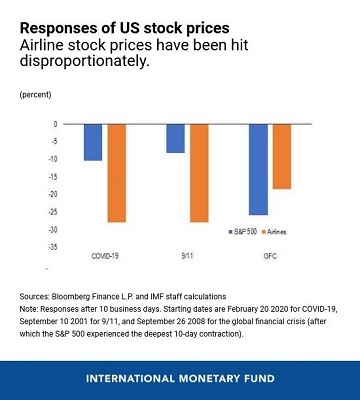
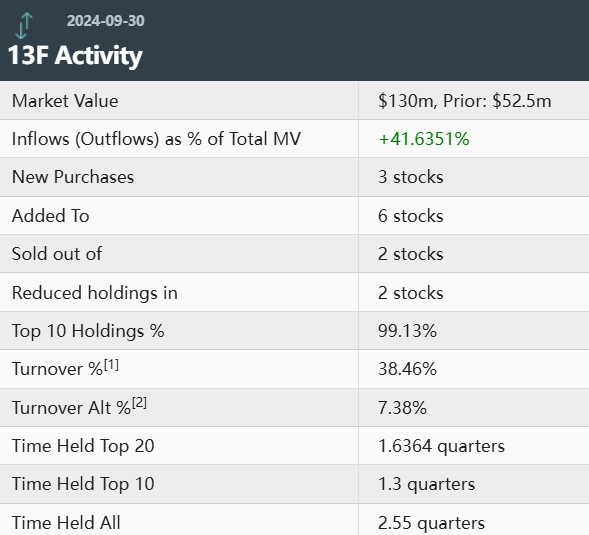
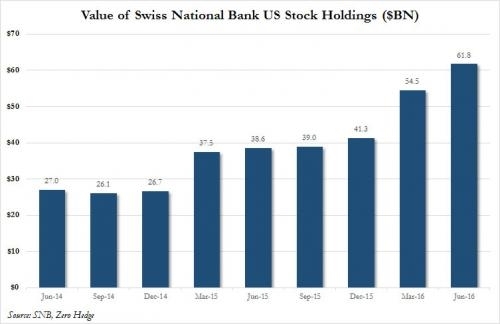
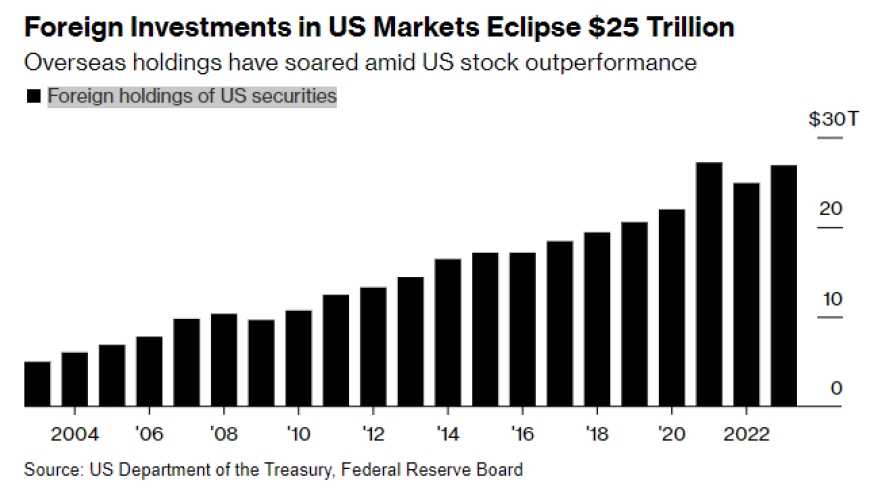
Understanding the Basics of the US Stock Market
The United States stock market, often referred to as the "Wall Street," is one of the most significant financial markets in the world. It plays a crucial role in the global economy, allowing investors to buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. If you're new to investing or simply curious about how the stock market operates, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the US stock market.
What is the Stock Market?
The stock market is a platform where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. These shares represent ownership in the company, and investors can purchase them to become part owners. The US stock market is divided into two primary exchanges: the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ.
How Does the Stock Market Work?
Listing a Company on the Stock Exchange: Before a company can be listed on a stock exchange, it must go through an initial public offering (IPO). During the IPO, the company sells shares to the public for the first time, raising capital to fund its operations and expansion.
Trading of Shares: Once a company is listed, its shares can be traded on the stock exchange. Investors can buy and sell shares through a broker, who acts as an intermediary between the buyer and seller. The price of each share is determined by supply and demand in the market.
Market Orders and Limit Orders: Investors can place two types of orders when buying or selling shares: market orders and limit orders. A market order is an order to buy or sell at the best available price, while a limit order is an order to buy or sell at a specific price or better.
Market Capitalization: The market capitalization of a company is the total value of its outstanding shares. It is calculated by multiplying the number of shares outstanding by the current market price. Companies with high market capitalizations are often considered large-cap stocks, while those with lower market capitalizations are considered small-cap or micro-cap stocks.
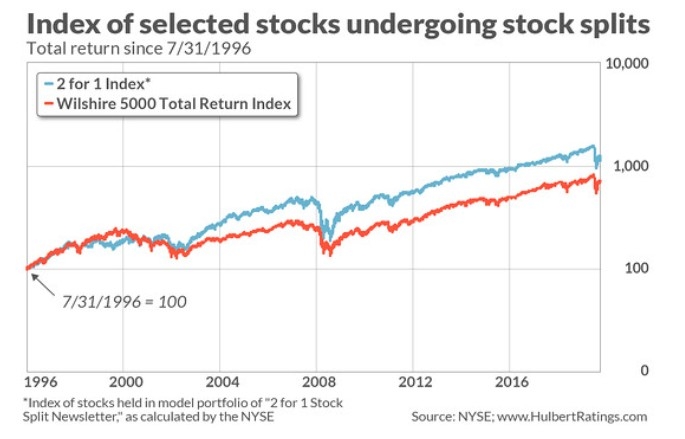
Dividends: Some companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividends can be paid in cash or additional shares of stock and are often used as a measure of a company's financial health.
Key Factors Influencing the Stock Market:
Economic Indicators: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation can significantly impact the stock market. A strong economy often leads to higher stock prices, while a weak economy can cause stock prices to fall.
Corporate Earnings: The financial performance of companies is a critical factor in the stock market. Companies that report strong earnings can see their stock prices rise, while those with poor earnings may see their stock prices fall.
Political Events: Political events, such as elections or changes in government policies, can also impact the stock market. Investors often react to political uncertainty by selling off their investments.
Global Events: Global events, such as trade wars or geopolitical tensions, can also have a significant impact on the stock market. Investors often react to these events by seeking safer investments, such as gold or government bonds.
Case Study: Facebook's IPO
In 2012, Facebook, one of the world's largest social media platforms, went public in what was then the largest IPO in history. The company raised
In conclusion, the US stock market is a complex and dynamic financial marketplace that offers investors numerous opportunities to grow their wealth. By understanding the basics of how the stock market works, you can make informed investment decisions and potentially achieve financial success.
new york stock exchange
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....