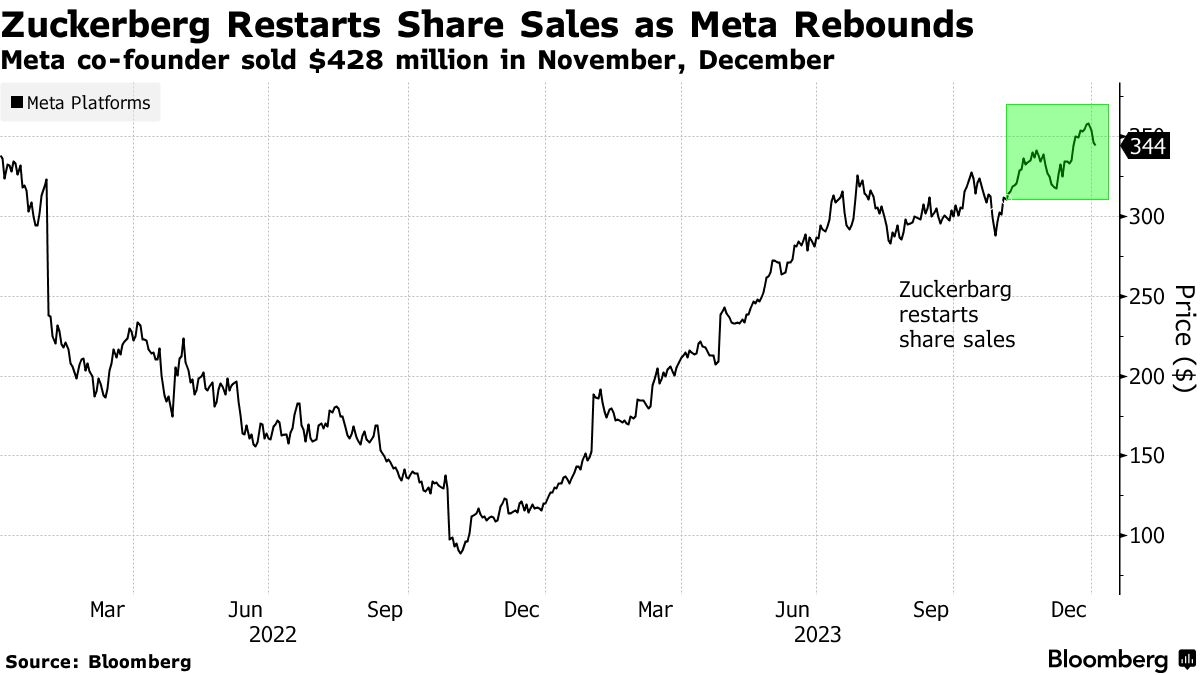
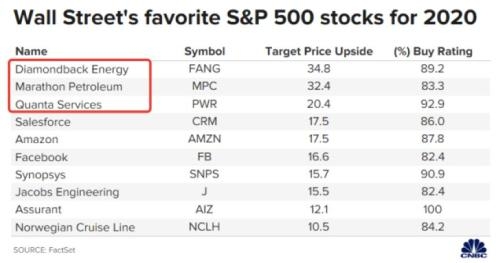
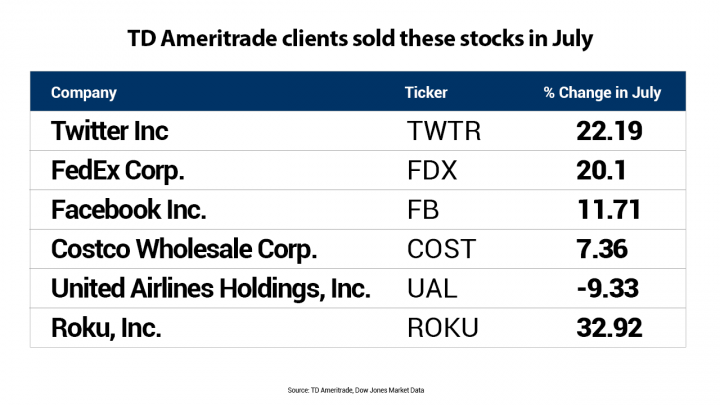
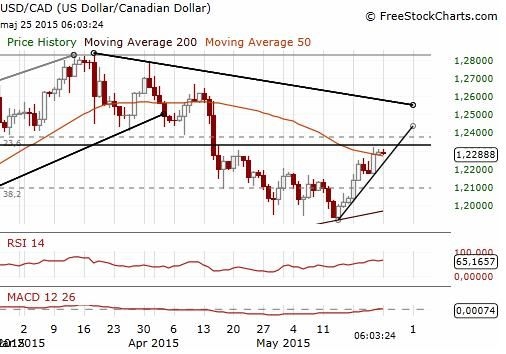
Have you ever wondered if the U.S. government issues stocks? It's a question that often comes up, especially among investors and financial enthusiasts. The answer is both straightforward and complex. Let's delve into the details to understand the role of the U.S. government in the stock market.
Understanding Government Securities
Firstly, it's important to differentiate between stocks and government securities. Stocks represent ownership in a company, while government securities are debt instruments issued by the government to finance its operations.
The U.S. government primarily issues two types of securities: Treasury bills, Treasury notes, and Treasury bonds. These securities are not stocks, but they are still a crucial part of the financial market. They are considered to be among the safest investments due to the government's ability to tax and print money.
The Role of the U.S. Treasury
The U.S. Treasury is responsible for managing the government's finances, including the issuance of securities. When the government needs to finance its operations, it issues these securities to investors. This process helps the government raise funds without increasing its debt burden.
Why the Government Does Not Issue Stocks
Now, let's address the main question: why doesn't the U.S. government issue stocks? The primary reason is that the government is not a for-profit entity. Its main objective is to serve the public and provide essential services. Unlike private companies, the government does not aim to maximize profits or shareholder value.
Additionally, issuing stocks would complicate the government's financial structure. It would require the government to manage shareholder rights, dividends, and other corporate governance issues. This would divert resources from its core responsibilities.
Government Investment in Companies
While the government does not issue stocks, it does invest in private companies. This investment is usually done through various government agencies and programs. For example, the Small Business Administration (SBA) provides loans and guarantees to small businesses, helping them grow and create jobs.
Case Study: Government Investment in Tesla
A notable example of government investment in a private company is the U.S. government's investment in Tesla. In 2009, the Department of Energy provided $465 million in loans to Tesla to help the company develop its electric vehicle technology. This investment played a crucial role in Tesla's growth and success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the U.S. government does not issue stocks. Instead, it focuses on managing its finances through the issuance of government securities. While the government does invest in private companies, this investment is aimed at supporting economic growth and job creation, rather than maximizing profits. Understanding this distinction is crucial for anyone interested in the financial markets and the role of the government in them.
google stock price
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....