Introduction: In the United States, depreciation is a crucial aspect of accounting and tax laws that affects businesses of all sizes. The depreciation rates for capital stock are a key component of financial reporting and tax calculations. Understanding these rates is essential for businesses to manage their assets effectively and comply with regulatory requirements. This article delves into the intricacies of US depreciation rates for capital stock, providing insights and practical examples to help you navigate this complex area.
What is Depreciation? Depreciation is the systematic allocation of the cost of an asset over its useful life. It represents the reduction in the value of an asset due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or other factors. In the United States, depreciation is a non-cash expense that businesses can deduct from their income for tax purposes.
Depreciation Methods: There are several depreciation methods recognized under US tax law, including:
Straight-Line Depreciation: This method allocates an equal amount of depreciation expense each year over the asset's useful life. It is the simplest and most commonly used depreciation method.
Accelerated Depreciation: This method allows businesses to expense a larger portion of an asset's cost in the early years of its life. There are various accelerated depreciation methods, such as the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS).
Sum-of-the-Years'-Digits (SYD) Depreciation: This method allocates depreciation based on the sum of the asset's useful life in years. The depreciation expense is highest in the first year and decreases each year.
Double-Declining Balance Depreciation: This method accelerates depreciation by applying a constant percentage to the asset's book value each year.
Depreciation Rates for Capital Stock: The depreciation rates for capital stock vary depending on the asset's classification and useful life. Here are some examples:
Real Property: Real property, such as buildings and land improvements, typically has a useful life of 27.5 years for residential property and 39 years for commercial property.
Personal Property: Personal property, such as equipment and furniture, has a useful life ranging from 3 to 15 years, depending on the type of asset.
Automobiles: Automobiles have a useful life of 5 years for passenger vehicles and 7 years for commercial vehicles.
Example:
Let's consider a business that purchases a piece of equipment for
Importance of Accurate Depreciation: Accurate depreciation is essential for several reasons:
Tax Planning: Proper depreciation allows businesses to reduce taxable income, potentially resulting in lower tax liabilities.
Financial Reporting: Depreciation is a key component of financial statements, providing stakeholders with insights into the company's asset base and financial health.
Asset Management: Understanding depreciation helps businesses make informed decisions about asset replacement and maintenance.
Conclusion: Understanding US depreciation rates for capital stock is crucial for businesses to manage their assets effectively and comply with tax regulations. By familiarizing yourself with the different depreciation methods and rates, you can make informed decisions about asset management and tax planning. Always consult with a tax professional or accountant for personalized advice and guidance.
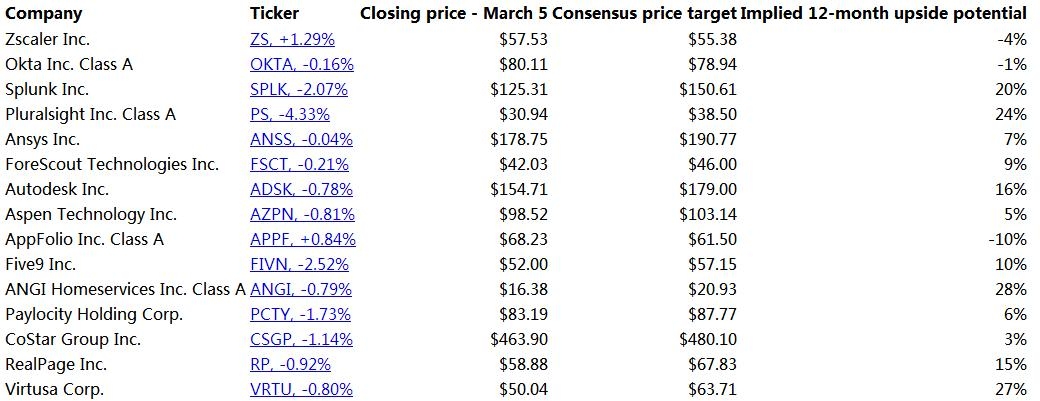
us stock market today live cha
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....