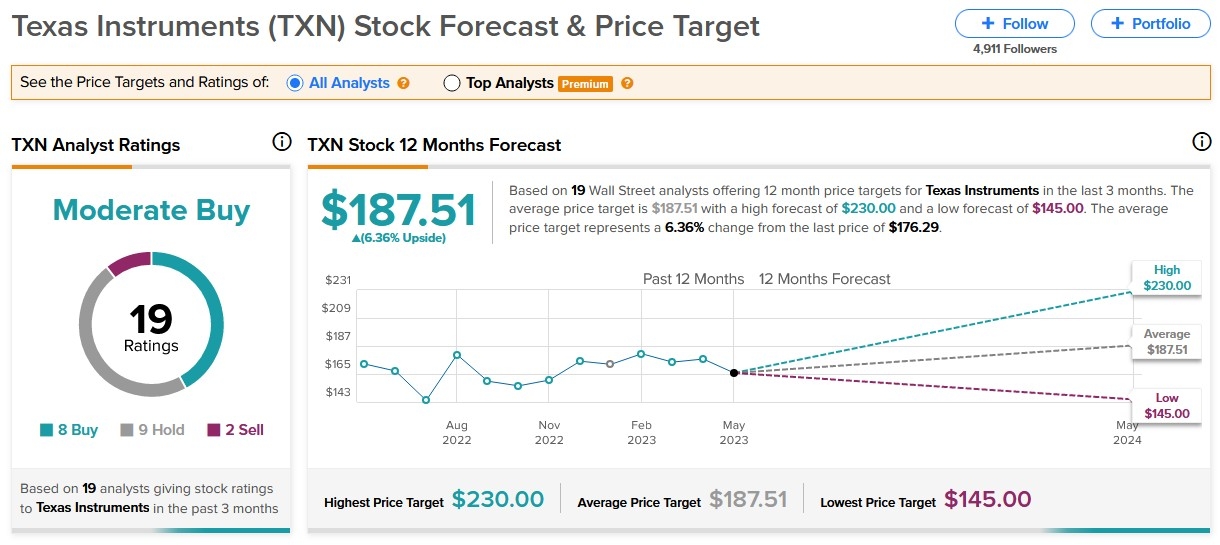
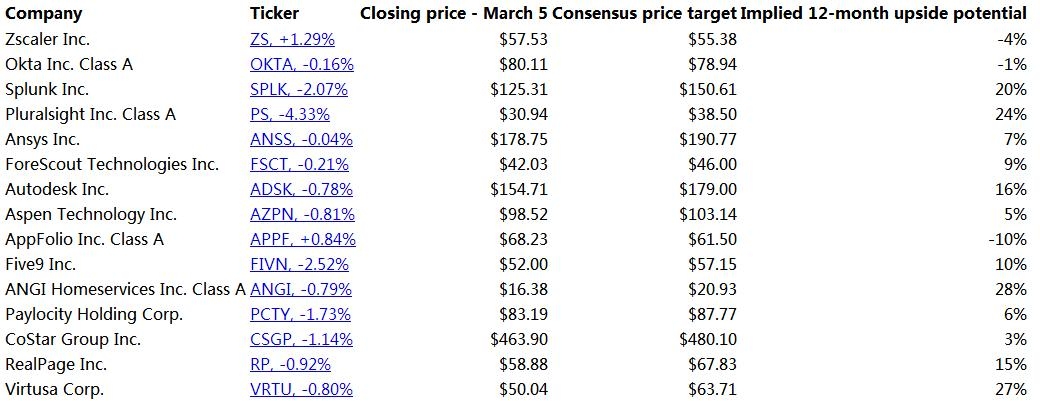
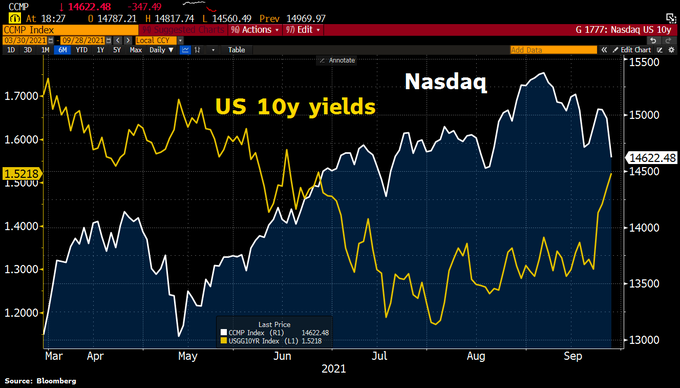
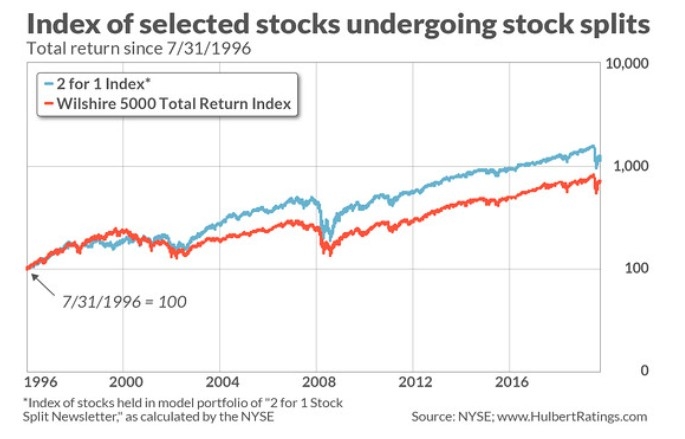
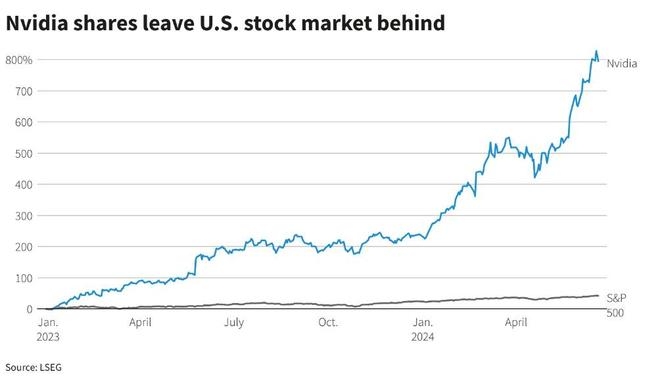
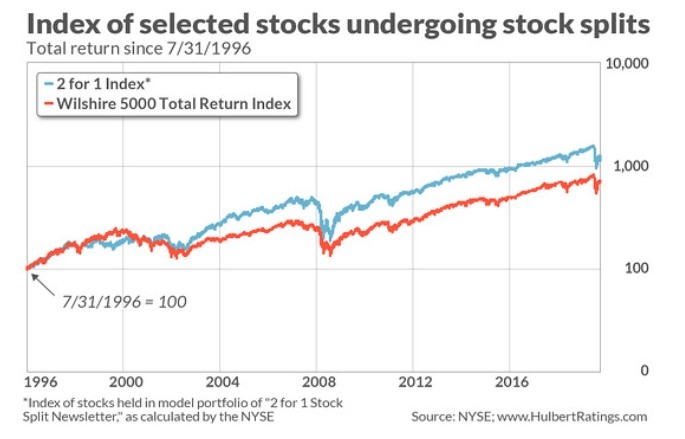
The stock market is a crucial indicator of the economic health and performance of a country. In the United States, the stock market is measured using various indices that reflect the overall performance of the market. Understanding how these indices are calculated can help investors make informed decisions. In this article, we will explore the different methods used to measure the stock market in the US.
The S&P 500 Index
One of the most widely followed stock market indices in the US is the S&P 500. This index consists of 500 large-cap companies from various sectors, including technology, healthcare, and finance. The S&P 500 is a market capitalization-weighted index, meaning that the weight of each company in the index is determined by its market value.
Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is another well-known stock market index in the US. It consists of 30 large-cap companies across various sectors, including transportation, energy, and technology. The DJIA is a price-weighted index, which means that the value of each stock in the index is weighted by its price.
The NASDAQ Composite
The NASDAQ Composite is an index that tracks the performance of all stocks listed on the NASDAQ exchange. It includes companies from various sectors, including technology, biotechnology, and retail. The NASDAQ Composite is a market capitalization-weighted index, similar to the S&P 500.
The Russell 3000 Index
The Russell 3000 Index is a broader index that includes the 3,000 largest US companies by market capitalization. It provides a more comprehensive view of the US stock market than the S&P 500 or the DJIA. The Russell 3000 is a market capitalization-weighted index, similar to the S&P 500.
Measuring the Stock Market's Performance
To measure the performance of the stock market, investors and analysts often use a variety of metrics. These metrics include:
- Return on Investment (ROI): This metric measures the profitability of an investment over a specific period.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS is a measure of a company's profitability, calculated by dividing the company's net income by the number of outstanding shares.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: The P/E ratio compares a company's stock price to its EPS, providing insight into the market's valuation of the company.
Case Study: Apple Inc.
Let's take a look at a case study involving Apple Inc., a company that is often used as an example of a successful stock market investment. Apple is a component of the S&P 500 and the NASDAQ Composite indices.
In 2010, Apple's stock price was around
Using the ROI metric, an investor who bought Apple stock in 2010 and sold it in 2015 would have seen a return of approximately 45%. This example illustrates how the stock market's performance can be measured using various metrics.
In conclusion, the stock market in the US is measured using a variety of indices and metrics. Understanding how these indices are calculated and how to interpret them can help investors make informed decisions. By keeping an eye on the S&P 500, DJIA, NASDAQ Composite, and other indices, investors can gain valuable insights into the overall performance of the stock market.
us stock market live
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....