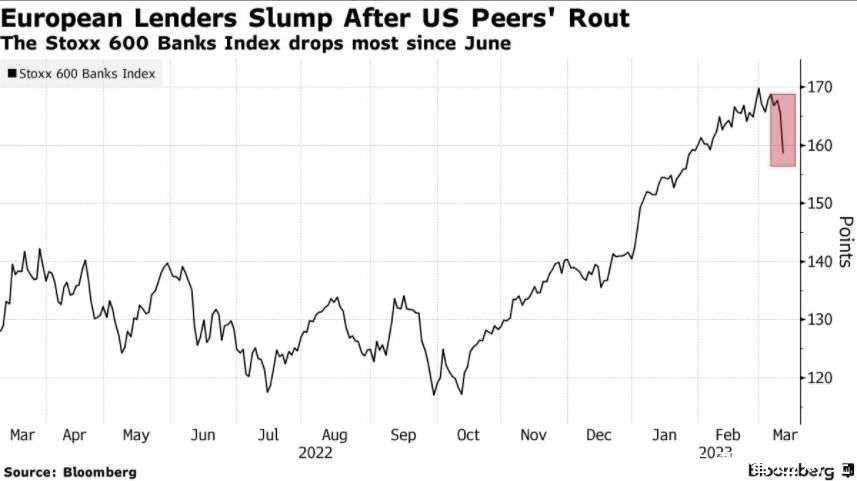
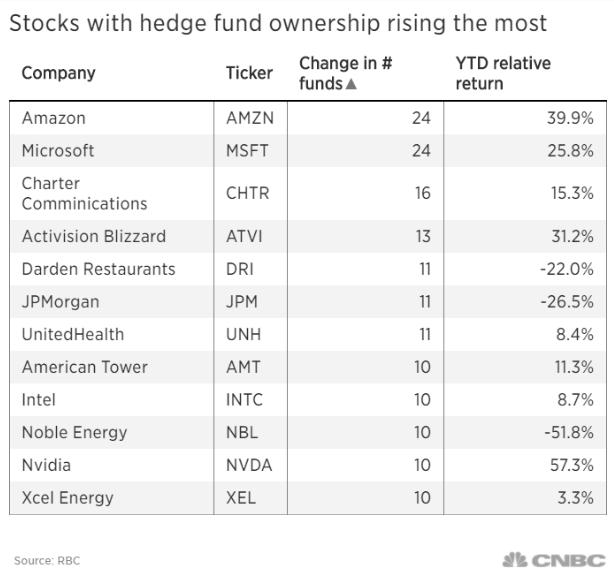
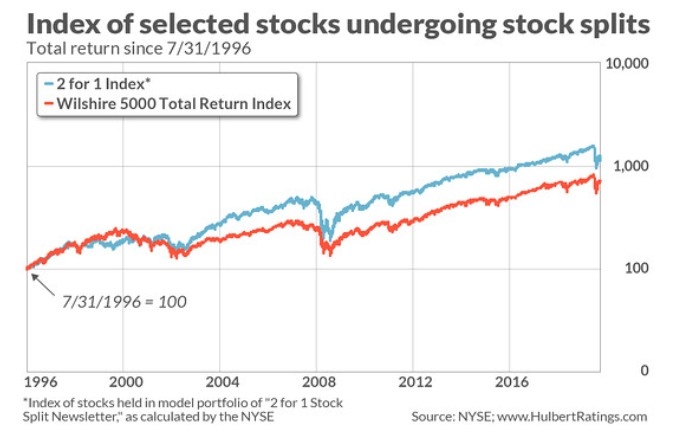
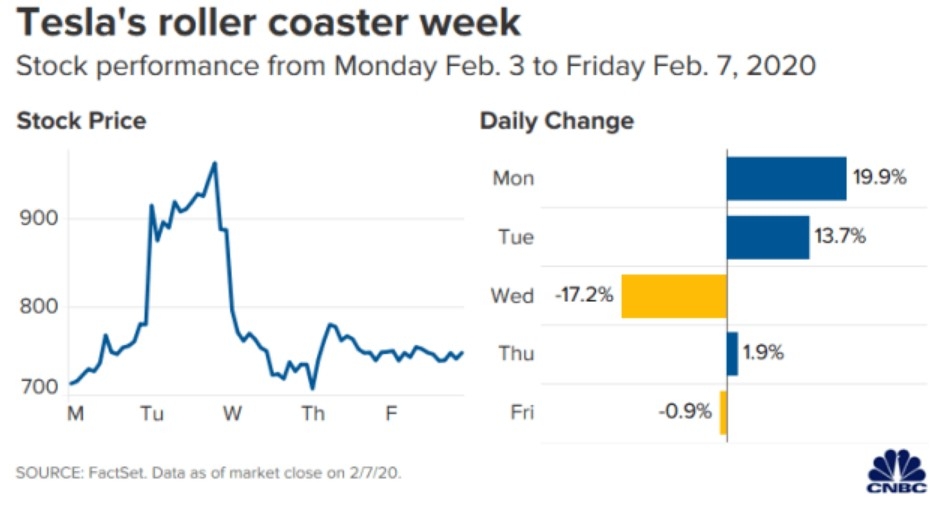
Introduction:
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, stock index options have emerged as a powerful tool for investors looking to hedge risks or capitalize on market movements. Understanding the intricacies of US stock index options can be the difference between a successful investment strategy and a costly mistake. This comprehensive guide will delve into the basics of trading US stock index options, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding US Stock Index Options:
What Are US Stock Index Options?
US stock index options are contracts that give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific stock index at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified period (expiration date). These options are a form of derivative, derived from the underlying stock index, which represents a basket of stocks.
Types of US Stock Index Options:
- Call Options: These options give investors the right to buy the underlying stock index at the strike price before the expiration date. Call options are typically purchased when investors expect the stock index to rise in value.
- Put Options: These options give investors the right to sell the underlying stock index at the strike price before the expiration date. Put options are often purchased when investors anticipate a decline in the stock index's value.
Benefits of Trading US Stock Index Options:
- Hedge Against Market Volatility: Investors can use stock index options to protect their portfolios from adverse market movements. For example, purchasing put options on a stock index can limit potential losses if the market declines.
- Leverage: Options trading allows investors to control a larger amount of stock index exposure with a smaller investment compared to direct stock purchases.
- Limited Risk: Unlike stock trading, where an investor's risk is unlimited, options trading is limited to the premium paid for the option contract.
Strategies for Trading US Stock Index Options:
- Covered Call: This strategy involves owning the underlying stock index and selling call options on it. It generates income from the premium received, while limiting the upside potential.
- Protective Put: This strategy involves owning the underlying stock index and purchasing put options to protect against potential declines in the market.
- Straddle: This strategy involves purchasing both a call and a put option on the same stock index with the same strike price and expiration date. It is used when an investor expects a significant price movement in either direction.
Case Study:
Consider an investor who owns a portfolio of stocks and wants to hedge against market volatility. The investor purchases a put option on the S&P 500 index with a strike price of 3,500 and an expiration date of three months. If the market declines and the S&P 500 index falls below the strike price, the put option will increase in value, mitigating the investor's losses in the stock portfolio.
Conclusion:
US stock index options offer a versatile and powerful tool for investors to manage risks and capitalize on market movements. By understanding the basics of trading options, investors can develop a well-rounded investment strategy that aligns with their financial goals.
new york stock exchange
 google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....
google stock price-Access our proprietary algorithm that analyzes 5,000+ data points to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential. This tool is normally reserved for institutional clients.....